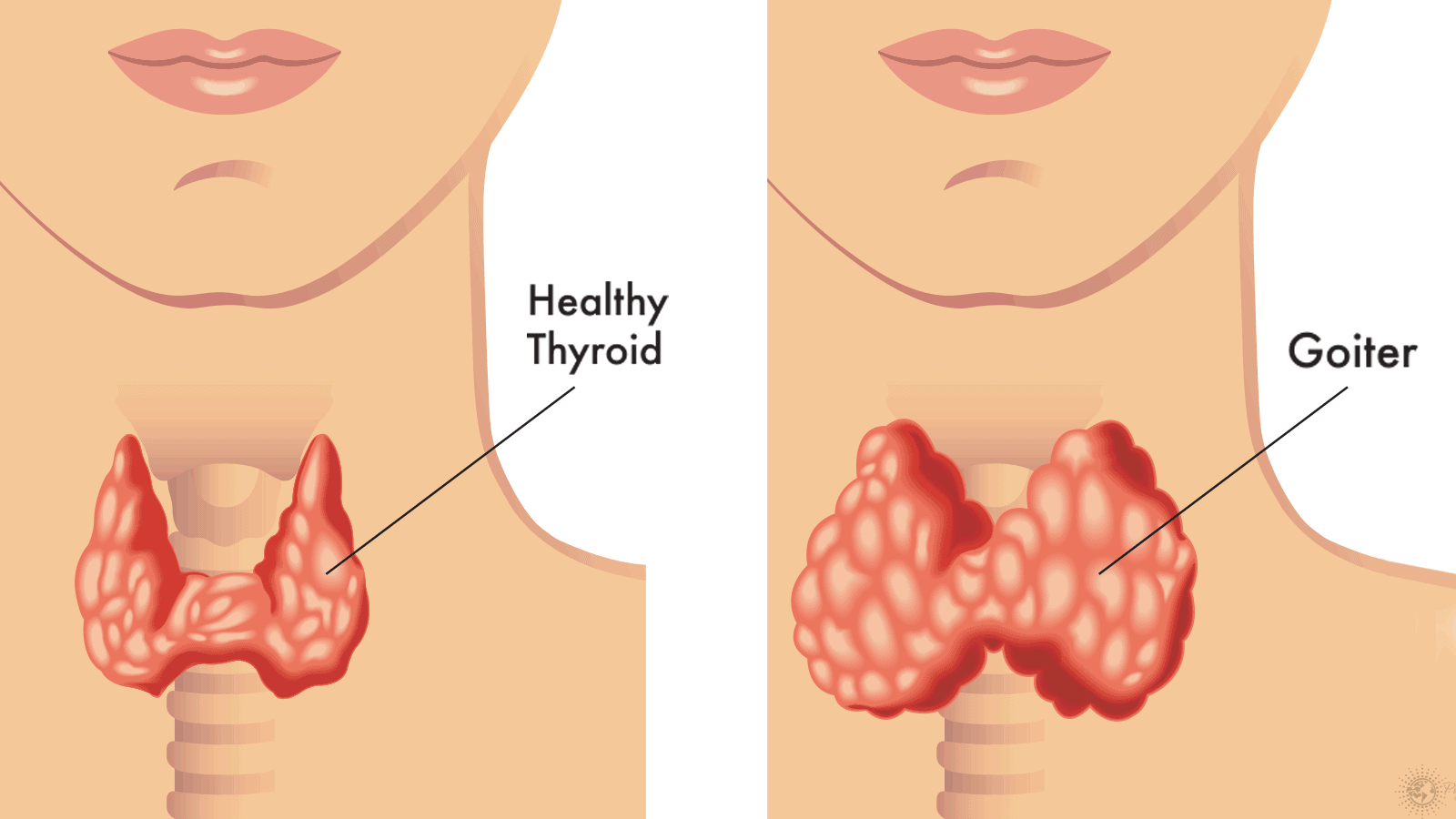
The two diseases that can affect how your thyroid gland functions include hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism. While the two may sound similar, the impact that they can have on the butterfly-shaped gland is markedly different. According to the National Institute of Health, more than 4 percent of Americans ages 12 and over have been diagnosed with hypothyroidism while 2 percent have been diagnosed with hyperthyroidism. For those who may not be familiar with the role that the thyroid gland plays in the human body, it is responsible for producing hormones that govern and regulate how the body uses energy, which, in turn, affects organ function. Studies have shown that the thyroid gland even affects the rhythm of your heart. In this article, we will explore the difference between hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism and how these diseases can affect your overall health. Also, we will detail the five things that everyone should know about this butterfly-shaped gland situated at the base of your neck.
HYPOTHYROIDISM VERSUS HYPERTHYROIDISM
To better understand how hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism can adversely affect your health, let’s take a closer look at these two diseases individually:
Hyperthyroidism – This condition is characterized by an overactive thyroid gland that produces a surplus of hormones that the body is incapable of using. Some of the more notable symptoms of hyperthyroidism include changes in appetite, fatigue, increased irritability, irregular heartbeat, diarrhea, and profuse sweating. It is also important to note that women who develop hypothyroidism may notice changes in their fertility as well as their menstrual cycle. To further complicate matters, women who are pregnant and have developed hyperthyroidism are at risk of the disease adversely affecting the health of their baby.
Hypothyroidism – Unlike hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism is characterized by an underactive thyroid in that the butterfly-shaped gland does not produce enough of the hormones required by the body for optimal health. Some of the more common side effects associated with hypothyroidism include constipation, fatigue, weight gain, muscles weakness, and xeroderma (dry skin). Additionally, hypothyroidism can cause hair loss and may result in low libido. Similar to hyperthyroidism, women who are pregnant and have developed the condition are also at risk of the disease potentially affecting the health of their baby. Studies also show that hypothyroidism can cause fertility problems for women who are trying to conceive.
WHAT CAUSES THYROID-RELATED PROBLEMS?
Having established some of the key differences between hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism, let’s take a moment to focus on the differences between them from an etiological standpoint. In most cases, hypothyroidism is a byproduct of Hashimoto’s disease, an autoimmune disease that attacks the thyroid and causes thyroiditis (inflammation), which reduces the number of hormones the gland is capable of producing. Another thing to note is that thyroiditis can take on many forms including subacute thyroiditis, which is generally precipitated by a bacteria or virus. Thyroiditis can also include postpartum thyroiditis, which can affect women following childbirth, and silent thyroiditis, an asymptomatic autoimmune condition that causes the gland to become enlarged. If thyroiditis is not resolved, it can result in hypothyroidism.
As far as hyperthyroidism is concerned, the disease can stem from a variety of health problems including thyroid-based nodules, thyroiditis, and Grave’s disease, an immune system disorder characterized by exophthalmos (swelling of the eyeballs) and swelling of the neck. Although rare, hyperthyroidism can also be caused by tumors affecting the pituitary gland or by consuming excessive amounts of iodine. Not too dissimilar from hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism can also be caused by subacute, postpartum, and silent thyroiditis as well. And in the same vein as hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism can complicate a woman’s pregnancy or trigger fertility problems. All in all, a poorly functioning thyroid causes a number of health problems for men and women alike.
TREATMENTS FOR THYROID-RELATED PROBLEMS
Treating hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism typically involves dietary changes, medication, and surgery. The approach to these treatments, however, can vary slightly depending upon whether you have been diagnosed with hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism. For example, an individual who has been diagnosed with hypothyroidism may be prescribed a medication that mimics the hormone that a healthy thyroid-based gland would produce naturally like levothyroxine, for example. Conversely, those diagnosed with hyperthyroidism may be prescribed beta blockers or antithyroid medications that can help decrease thyroid-based hormone production. Lastly, individuals with hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism are encouraged to speak with their physician regarding dietary changes that can help alleviate symptoms as they can be patient-specific.
WHEN SHOULD YOU CONSIDER SURGERY?
Considering that a poorly functioning thyroid causes a plurality of health problems, it should come as no surprise that many patients opt to have the butterfly-gland surgically removed. However, there are a few things that you should know about the surgical procedure first. For those diagnosed with hyperthyroidism, surgically removing the gland could lead to the development of hypothyroidism. In which case, you’re trading one thyroid-based problem for another one. There is also a similar downside when it comes to hypothyroidism in that the general anesthesia used during surgery may worsen your symptoms as opposed to improving them. In either case, it is a good idea to discuss the pros and cons with your physician before agreeing to undergo surgery. After all, there are several treatments available to those who have been diagnosed with either thyroid-based disease including radiation therapy.
WHAT EVERYONE SHOULD KNOW ABOUT THEIR THYROID-BASED GLAND
Having established the fact that a poorly functioning thyroid causes physiological changes that can adversely affect one’s health, let’s take a moment to recap the five things that everyone should know about this gland:
1. LOCATION
While it cannot be seen or felt, your thyroid-based gland is located in the lower region of your neck and produces hormones that allow the body to function properly, affecting cholesterol levels, body weight, breathing, and everything in between. Common signs that may suggest a problem with this gland is when it can be seen or felt. If you’re experiencing either of these symptoms, it would be in your best interest to schedule an appointment with a physician as soon as possible.
2. YOU ARE NOT ALONE
If you have been diagnosed with hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism, you can take solace in knowing that you are not alone as more than 20 million people in the U.S. have been diagnosed with some variation of a thyroid-based disease. Also, they are most likely struggling with many of the same symptoms including lack of focus, insomnia, managing their weight, and much more.
3. CHANGING YOUR DIET CAN HELP IMPROVE SYMPTOMS
While the dietary needs of those diagnosed with hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism can vary, making small changes to your diet can help soothe some of the symptoms that you may be experiencing. For example, it may be worth your while to restrict processed foods from your diet, which are loaded with sugar and sodium. These ingredients can worsen hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism symptoms and can also lead to other health problems like hypertension and obesity, for example.
4. THE BODY CAN SURVIVE WITHOUT THE THYROID-BASED GLAND
Although the butterfly-shaped gland that sits in the lower region of your neck plays a key role in many bodily functions, it is entirely possible for you to survive without it. However, you will have to take medication that mimics the hormone that would have ordinarily been produced by a healthy thyroid-based gland. It is worth noting, however, that this is not usually the first line of treatment. In most cases, dietary changes, prescription medication, and radiation therapy are more than enough to resolve symptoms associated with hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism.
5. IODINE CAN HELP IMPROVE HOW THE GLAND FUNCTIONS
As one of the essential minerals needed for good health, iodine can help improve how the thyroid-based gland functions. In fact, the butterfly-shaped gland uses this mineral to produce hormones that work to repair damaged cells, boost metabolism, and much more. The best way to boost your iodine levels is by consuming iodine-rich foods like shrimp, tuna, eggs, prunes, and seaweed, for example. Iodine can also be found in common table salt as well. Because these foods contain a fair bit of sodium, you should govern yourself accordingly. After all, too much sodium can lead to hypertension and other health problems.
In summation, hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism can significantly affect your overall quality of life; however, you needn’t fret as there are a number of treatments that can help resolve your symptoms including medications that can replicate the hormones that the thyroid-based gland produces naturally. Of course, if you’re experiencing symptoms that may be indicative of a thyroid-based problem, you’re encouraged to schedule an appointment with your physician who can make a formal diagnosis and prescribe a course of treatment that can help improve your health. Besides, a poorly functioning thyroid causes a variety of symptoms that serve as an indication that something is not quite right.