Anxiety is a normal human emotion that everyone feels from time to time. Anxiety is often a by-product of stress; which is something that we are all familiar with.
Battling anxiety on a daily basis can be exhausting and even result in an anxiety disorder.
“Anxiety is like a rocking chair. It gives you something to do, but it doesn’t get you very far.” – Jodi Picoult
Anxious feelings generally consist of the following:
-Feelings of panic, fear, and uneasiness
-Problems sleeping
-Cold or sweaty hands and/or feet
-Shortness of breath
-Heart palpitations
-An inability to be still and calm
-Headache
-Numbness or tingling in the hands or feet
-Stomach ache
-Muscle tension
– Dizziness
Neurochemical changes in the brain and environmental factors are considered the two biggest contributors to anxiety. Scientists have vehemently rejected personal weakness, character flaws, or a lack of maturity as being legitimate causes of anxiety.
Anxiety, if left unchecked, can affect our entire being; affecting how we feel, think and act, while having evident physical symptoms. Mild anxiety is relatively vague and uncomfortable, while severe anxiety can become debilitating. Therefore, it’s important to know what causes anxiety in order to limit or prevent it.
Here are 7 things known to cause anxiety, and ways to prevent it:
1. Stress
Without a doubt, stress is the biggest contributor to anxiety. Stressful situations happen to nearly everyone; as a consequence so does anxiety. Anything that poses a threat or challenge to our well-being is a stressor. While some stress is indeed good for us, battling frequently with stress can destabilize our mental and physical health.
Mental health professionals generally recommend three ways of coping with and treating stress: self-management, self-help, and medication.
Self-help methods include exercise, a healthy diet, being assertive (not saying yes to everything), breathing techniques, and expressing your thoughts and worries to someone.
Self-management techniques include learning about stress and anxiety (books, medical journals, etc.), stress management courses, and natural therapies such as aromatherapy.
Medication should be considered a last resort, but if physical and mental symptoms are in advanced states, doctors may prescribe an antidepressant or a beta-blocker, which helps to counteract the physical symptoms of anxiety. From there, you can begin to work your way backward through the other two methods, with the goal to end any medicated means altogether.
2. Caffeine
Caffeine is a stimulant that increases blood pressure, heart rate, and respiration. These symptoms are common when experiencing anxiety. Caffeine also fuels your “fight or flight” response, which can make anxiety much worse and even trigger an anxiety attack.
Moderate amounts of caffeine can bring some mental benefits – increased alertness, motivation, concentration, memory, and attention. The keyword here is moderation; no more than 400 mg over the course of a day. Too much caffeine triggers irritability, nervousness, restlessness, upset stomach, fast heartbeat, and muscle tremors.
As with nearly everything, use caffeine wisely and in moderation. This is certainly advisable if you have had problems with anxiety in the past.
3. Over the counter drugs and supplements
Common supplements such as weight-loss pills, fat burners, and pre-workout products can include heavy amounts of caffeine and other stimulants. Other products that may initiate anxiety include headache and migraine relievers, cough medicines and decongestants. Some popular herbal remedies such as guarana and ginseng may also cause or increase the symptoms of anxiety.
The best thing you can generally do here is to avoid “energy-boosting” pills and supplements altogether. Calories are consumed in food, and guess what… you burn calories when your body expends energy. The difference here is when you take into account what kinds of food you’re putting into your body. Are you running on 87 octanes or 93?
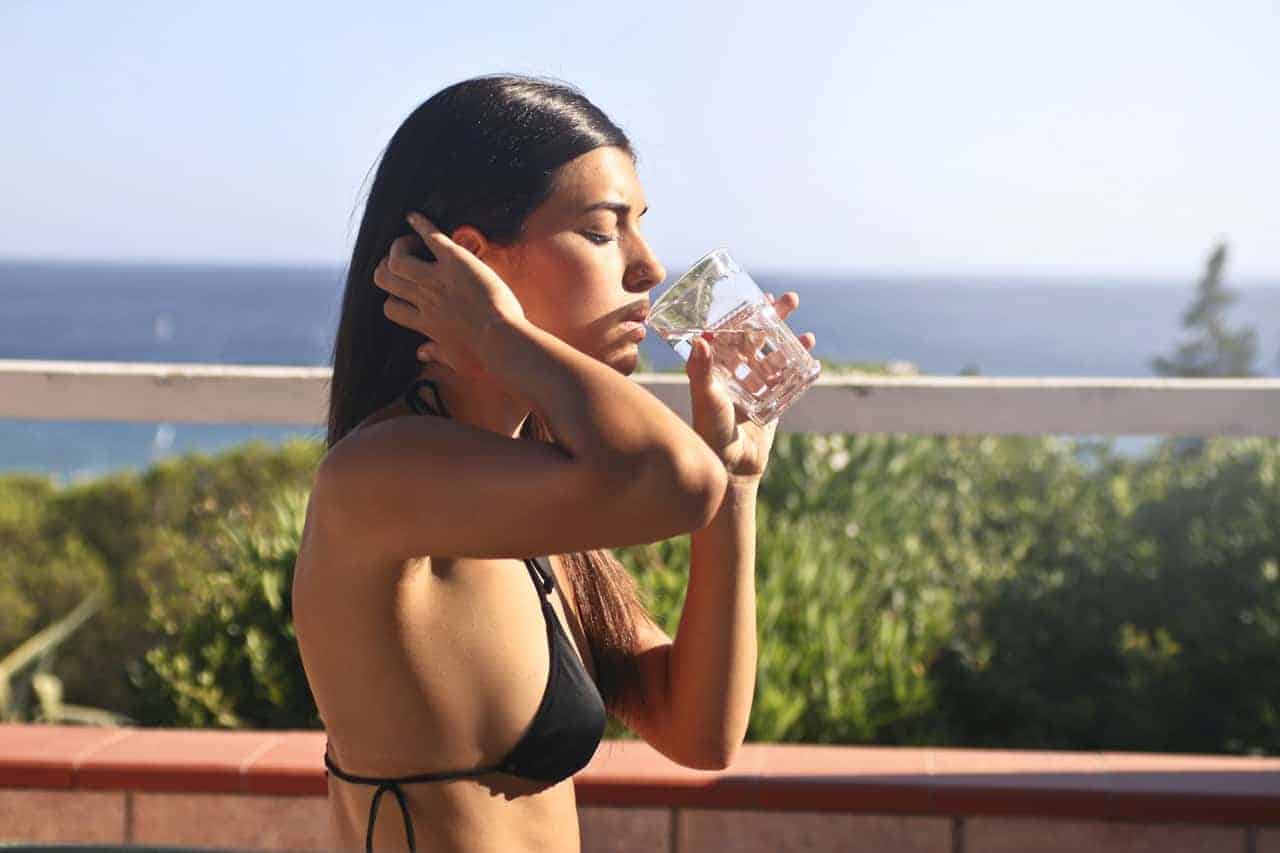
4. Dehydration
Proper hydration is essential for healthy brain function. In a 2009 study at Tufts University, researchers directly linked feelings of anger, confusion, fatigue, and tension to mild dehydration in student athletes. All of these symptoms are common in people who experience anxiety.
In addition to being an essential element in healthy brain function, hydration is also necessary for healthy physiological function. Mild dehydration can cause high blood pressure, fast heartbeat, facial tics, shaking hands, weak and shaking voice, excessive sweating and facial swelling.
Professionals at the Mayo Clinic recommend that adult males drink 13 cups (3 liters) of water each day. It is recommended that adult females drink 9 cups (2.2 liters) of water a day.
5. Nutrient deficiency
Proper nervous system function requires adequate amounts of certain nutrients. Nutrient deficiency has been directly linked with increased anxiety.
B complex vitamins, omega-3, magnesium and calcium, potassium, selenium, Vitamin D, theanine and lactium, GABA, and zinc are considered essential for proper neurotransmitters and other brain functions. A well-balanced diet will generally provide these essential nutrients, but there are substitutes available to help supplement your diet if needed.
Dietitians, naturopathy specialists, and nutritionists are all knowledgeable in this area. They may be able to provide some insight into specific actions that you can take to ensure that you’re getting the recommended amounts of nutrients.
6. Skipping meals
A healthy diet is the best way to ensure that you’re getting proper nutrition. Because of our frenzied, overworked, and stressed out work culture, it is common for people to skip a meal here and there.
The negative effects are cyclical in that people who live a frantic lifestyle are much more prone to anxiety and stress – symptoms which may cause them to not feel hungry. Not feeling hungry leads to skipping meals which throws off the body’s blood sugar levels. A prolonged drop in these levels results in increased anxiety and stress. This cycle is continuous until the person either: (a) alters their diet, or (b) stops feeling anxious and stressed.
Since ‘b’ is usually not an option, the only other answer is to change your eating habits. If you find it difficult to eat a full meal for whatever reason, make sure to have at least a healthy snack available. Snacks that contain healthy carbs and proteins are highly recommended.
7. Nicotine and alcohol
Nicotine is a stimulant that raises blood pressure and heart rate, which can lead to anxiety. Further, cigarettes and vapes contain carbon monoxide which can result in breathing problems – this can lead to the body reacting in a way that resembles oxygen deprivation. When we are deprived of oxygen, neither the brain nor the body can function properly.
As with most of the causes listed, the use of nicotine and alcohol is an incessantly negative cycle. People that have continuous stress and anxiety lean more on these substances than the rest of the population. According to the Anxiety and Depression Association of America, people who suffer from an anxiety disorder are two to three times more likely to abuse legal and illegal substances.
Multiple studies have shown the detrimental effects of nicotine use, especially smoking. Quitting any kind of nicotine use is the only viable alternative to counteract these effects. Medical experts recommend that if you choose to drink alcohol that you do so in moderation. For healthy adults, this means no more than two drinks a day.
Share How You Cope With Anxiety
Join the discussion: What are some other anxiety-inducing options that you haven’t read in this article? Help the community by identifying them in the comments below.