It’s no secret that exercise can be tough, especially if you aren’t used to it. Finding the motivation to get started can be even tougher. Despite how hard it is, we still must do it. It’s essential to human life to get up and move.
The consequences are dire if you don’t get adequate physical activity. At first, you may not notice what’s happening to your body. Eventually, it will become visible. Mirrors don’t lie. When it becomes apparent, that means some damage may already have been done.
So what exactly does lack of physical activity do to your body? Scientists explain in detail what happens to your body when you don’t get enough physical activity. Keep reading to find out more.
Mental & Emotional Consequences
While the activity of exercising is physical, it can have severe mental and emotional consequences. The good news is that it’s easier to get rid of mental and emotional outcomes than it is to get rid of physical effects (discussed further along in the article). Simply beginning an exercise regimen, no matter how small, can alleviate many of these consequences listed below.
Lack of Motivation
You may think that you need the motivation to start exercising, but in truth, a lack of it leads to a lack of motivation. You begin letting yourself go, and before you know it, you can get into a sense of feeling as if you don’t “deserve” to do better or to be motivated.
Kathy Smith, famous in the 1980s for her aerobics videos and fitness classes, said in an interview with BeliefNet, “It rescued me from a path that could have been partying and playing and low self-esteem and just not taking care of myself and getting into the wrong crowd…and I would say that this was my salvation. It rescued me from an unhealthy lifestyle.”
Adequate physical activity leads to motivation for other areas in your life.
Depression & Anxiety
Lack of physical activity doesn’t directly cause depression and anxiety. However, it is a solution to depression and anxiety, so without adequate physical activity, you could be setting yourself up to sink into mental despair. This is true even if you don’t already suffer from depression and anxiety. Lack of exercise can be an introduction to these psychological problems.
The effects of this are even more significant if you’ve had an adequate amount of physical activity in the past, but you stopped it. Studies support the theory that stopping exercise can lead to an increase in depression.
Decreased Cognitive Functioning
Lack of physical activity can lead to a decline in cognitive functioning over time. This decline can manifest in mental diseases such as Alzheimer’s or dementia later in life. Many people never think about how a lack of exercise can affect their minds because, on average, the effects don’t become evident until they’re in their 60s or later. While this correlation has been scientifically proven, the odds can easily be reduced by increasing regular physical activity earlier in life.
Physical Consequences
The physical consequences of a lack of adequate physical activity are what gets noticed most often and, consequently, what would prompt someone to increase their physical activity. Like many of the mental consequences, physical consequences can be stopped in their tracks. Here are three of the most common.
Uncontrollable Food Cravings
The link between lack of physical activity and uncontrollable food cravings may not be visible, but they are scientifically proven. There are two parts to this.
The first part is that increasing physical activity will cause a person to crave more food (energy) to replace the lost energy. This type of food craving isn’t wrong – these are sustaining food cravings because you’re burning so many calories. However, you must make healthy food choices. Otherwise, your increase in physical activity will be for nothing.
There is evidence that exercising right before a meal can decrease the amount of food that a person would want in one sitting. This data indicates that while an increase in physical activity will make you hungrier more often, you won’t eat as much in one sitting. Overall, increased physical activity leads to fewer food cravings.
Conversely, lack of physical activity leads to uncontrollable food cravings, especially for unhealthy foods. This desire is because as you gain weight, your body begins to crave more and more food to satisfy your caloric requirements. If you’re eating the wrong foods, it’s worse. Foods like sugary carbohydrates can be addictive, making you want more and more.
The point of both of these scenarios is that scientists and medical experts agree that adequate physical activity can reduce bad food cravings.
The Most Obvious Consequence: Weight Gain
Weight gain is the number one consequence of not getting enough physical activity. The reason for this is that it throws off the balance of calories in/calories out.
It’s a simple formula. If you eat the same amount of calories you burn, there is no weight gain or no weight loss. If you take in more calories than you lose, weight gain will occur. A lack of physical activity means that you’ll likely take in more calories than you burn.
Once counter to this is to eat lower calorie foods. For most people, this will slow your weight gain, but without proper physical activity, the weight gain will still slowly eventually creep in. There simply is no substitution for adequate physical activity.
Weight gain is a problem – but the biggest issue is that it leads to more dangerous health problems. There have been plenty of medical studies, and scientific evidence published that outlines these problems.
Health Consequences: Diseases and Conditions
Whether you gain weight or not due to lack of exercise, scientists have found evidence that there is a high risk of health problems without regular physical activity. As these health problems occur, they can get worse as you continue to live without daily physical activity.
Heart Disease
Heart disease, also known as cardiovascular disease, is one of the major killers among health conditions. An increase in fat cells, especially around the waist (known as visceral fat), makes heart disease much worse. According to the Center for Disease Control (CDC), one person dies from cardiovascular disease in the United States every 37 seconds. It’s a very alarming mortality rate and unfortunate since it can be prevented with regular physical activity, often.
Common types of cardiovascular disease that can occur from lack of physical exercise include:
- Coronary Artery Disease (most common and most deadly)
- Heart Attack
- High Blood Pressure
- Stroke
- Congestive Heart Failure
According to Chiadi Ndumele M.D., M.H.S., the Assistant Professor of Medicine at Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, “In everyday terms our findings suggest that consistently participating in the recommended 150 minutes of moderate to vigorous activity each week, such as brisk walking or biking, in middle age may be enough to reduce your heart failure risk by 31 percent.” This is a small amount of physical activity to incorporate into your life to keep those fat cells at bay and prevent shortening your life span.
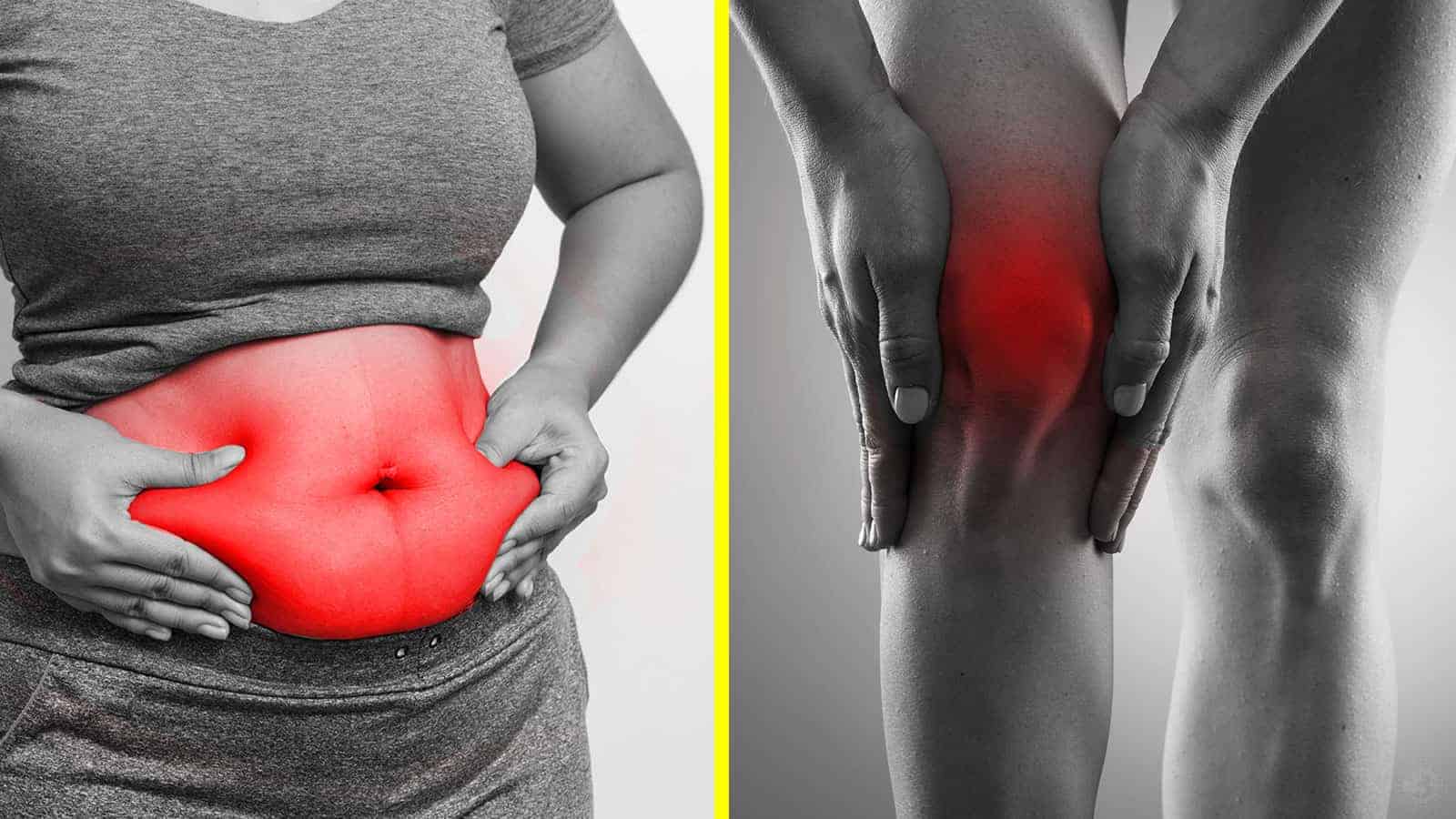
Joint & Bone Problems
Physical activity contributes to the health of joints and bones more than you realize. It encourages the production and distribution of synovial fluid. The synovial membrane which surrounds your joints produces this substance. Think of this fluid as a lubricant for your joints, keeping them from rubbing together, causing joint pain, and degrading over time.
Physical activity increases blood flow, which gets distributed to your joints better when you’re active. Autophagy is a condition triggered when you do regular physical activity. This is a process that essentially removes damaged cells in the joints so that new cells can be generated. It also helps to prevent joint pain.
Without these processes, including others that aren’t mentioned here, your joint and bone health can decline over time. You can begin to suffer from problems like arthritis and osteoporosis. Physical activity keeps you from having to worry about these inconveniences.
Muscle Atrophy
Muscle atrophy is a condition where your muscles waste away due to lack of activity. This commonly happens when people have injuries, are paralyzed, or have other problems that prevent movement of certain body parts. However, a lighter version of this condition – weakened muscles – can occur if you don’t do physical activity regularly.
You can see weakened muscles easily – people who work out are strong. People who don’t are weak. However, over time, it can become more serious than just not being able to bench press a lot of weight. It’s a situation of “use it or lose it.”
 Final Thoughts on the Importance of Prioritizing Exercise
Final Thoughts on the Importance of Prioritizing Exercise
All it takes is a look at all the scientific research and evidence to see why physical activity needs to be a regular part of your life. This doesn’t mean everyday activities like chores or walking around your office. It needs to be at least 150 minutes of vigorous activity each week. No matter how uncomfortable physical activity is, it’s a small inconvenience to prevent stroke, heart attack, depression, or any of the other problems that could happen.