Sleep, or a lack of it, is proven to be linked to clinical depression. Insomnia is widespread in the US and affects one out of every three adults at some point in their life.
It is more common in older adults (usually due to chronic physical illness) and women (who experience significant hormonal changes throughout their lives).
Insomnia is often a key characteristic in diagnosing depression. The inability to get to sleep or maintain it throughout the night is a critical contributing factor to the onset of depression.
When you feel sad or hopeless because of a personal situation, these feelings can cause insomnia as those thoughts spin around your head at a thousand miles an hour.
Those feelings can be overwhelming and persistent and you cannot fall asleep or stay asleep. Sleep is a restorative state where your body and mind recharge from the day’s events.
If that state is interrupted, you will feel fatigued, which leads to a lack of exercise and a declining fitness level. This can cause a vicious cycle of inactivity and sleeplessness.
Here’s How Many Hours of Sleep You Need To Avoid Depression
Lack of sleep can also stem from Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA), which interferes with sleep and prevents the person from experiencing restorative sleep. OSA interferes with the person’s airway and reduces oxygen supply to the body.
This causes the person to wake up often during the night. OSA links to the onset of depression. On the other hand, people with depression are five times more likely to have OSA symptoms.
Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD) is a form of depression triggered when the days begin getting shorter during the fall season. Shorter days mean less sunlight. In turn, less sunshine can harm a person’s circadian rhythm.
The circadian rhythm is a biological process that keeps us on a regular schedule.
When something disrupts the rhythm, it can cause insomnia and other sleep disorders, contributing to depression. Most people with SAD can eliminate symptoms with the onset of springtime and more sunshine.
Lack of slumber or the interruption of sleep can lead to depression or contribute to a depressive state lasting longer.
Improve Your Bedtime Routine by Doing These Things
So, what are some things we can do before bedtime to increase the chance of falling asleep and decrease the chances of waking up during the night? If you suffer from OSA, a continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) machine can increase airflow to your lungs and prevent you from waking up during the night due to compromised airways.
Meditation or listening to soft music before bed can increase relaxation and focus your mind on pleasant or emotionally neutral topics.
Please make a list of things you need to do the next day to help soothe your mind and prevent it from obsessing over your to-do list. When you write something down, your mind tends to let go of those concerns and forget about them, thus helping you get to sleep and stay asleep.
Exercise can help work out tension and relieve stress and fatigue in your body. Making sure you are tired at the end of the day can help you get to sleep. Furthermore, the endorphins released during exercise can stimulate your mood and lift your depression. Just limit activity to no later than a few hours before bed.
Yoga and deep abdominal breathing can lead to states of relaxation that will help you to get to sleep easier.
Limit caffeine, alcohol, and nicotine before you go to bed. These can act as stimulants and keep you from falling asleep quickly.
Keep your bedroom temperature cool, and take a warm shower right before bed so that your body will relax deeply as it cools.
The average adult needs between seven and nine hours of sleep per night to feel rested and prevent the symptoms of depression. Too little and you feel tired, irritable, and too much can lead to negative feelings and a deeper, longer-lasting depressive state.
Take care of your body, limit stimulating activities and foods right before bedtime, use techniques like meditation, yoga, and deep breathing to relax, and make sure your bedroom is set up to promote sleep.
Ten Other Ways That Sleep Benefits the Body
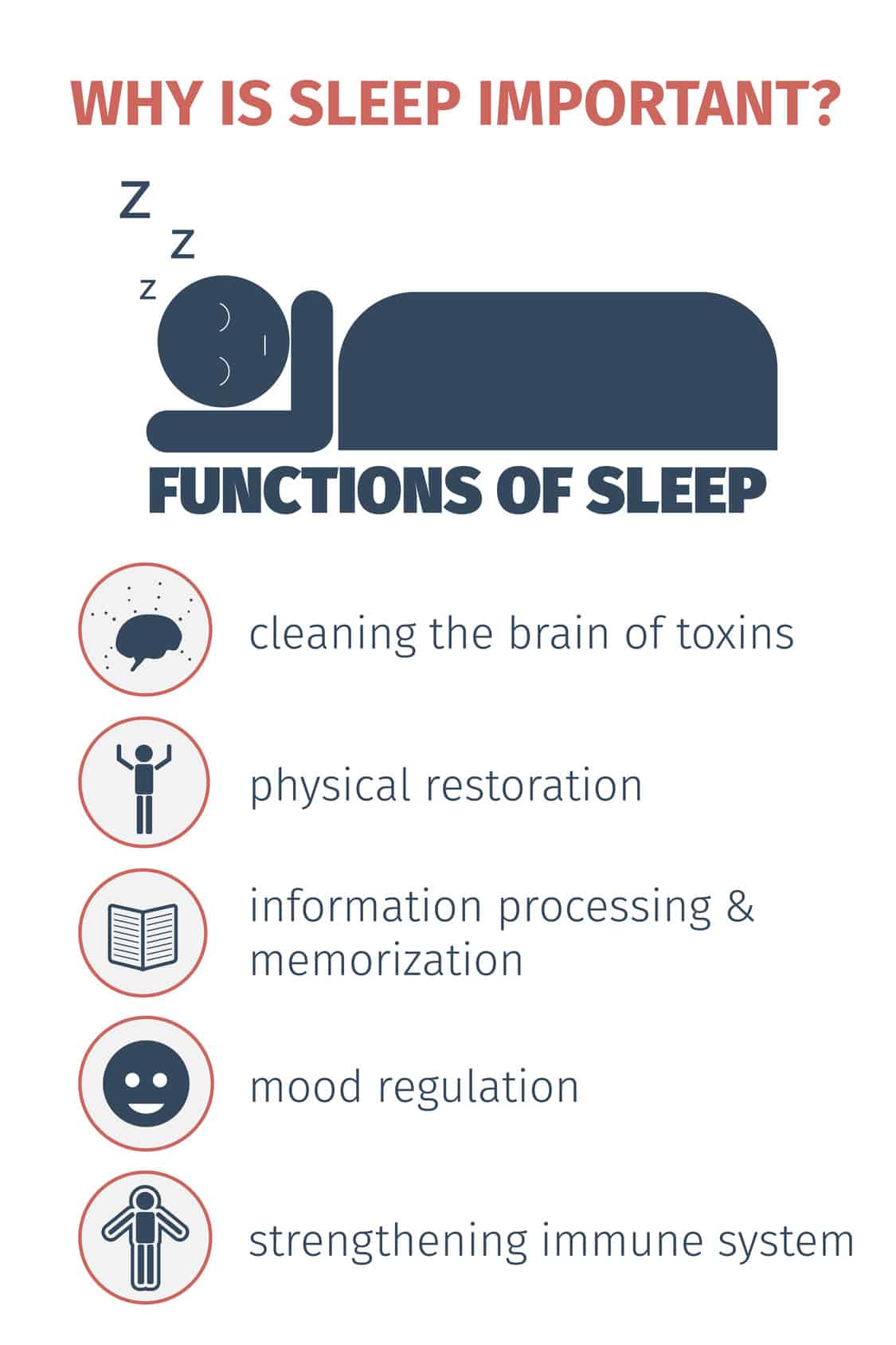
Besides avoiding depression, a good night of rest can provide these additional benefits.
1- Sleep reduces your chances of type 2 diabetes
While you sleep, your blood sugar drops. If you don’t get enough sleep in the deepest stages, it disrupts this process. It leaves you with too high of blood sugar. Your body has to work harder to respond to your cell’s needs. When you get deep sleep, you’re less likely to develop type 2 diabetes.
2 – Improve your immune system
Sleep helps your body fight off illness because it boosts your immune system. Lack of sleep changes your immune system, causing it to work overtime to protect your body. Getting a good night’s sleep prevents you from getting worn down so that your body can’t fight off viruses, infections, and other illnesses.
3 – Mental boosts come from getting enough sleep
If you’re sleep-deprived, you will have trouble focusing and remembering things. You can’t retain new information as well or recall details. Sleep plays a big part in your ability to learn and have good memory recall. Getting enough sleep gives your brain a break, store memories, and then pull these memories up later when you need them.
4 – Heart health
As you sleep, blood pressure is lowered, which rests on blood vessels and your heart. The less sleep you get, the longer your blood pressure stays up all day and night. High blood pressure can cause heart disease or stroke.
5 – Helps control your weight
When you’re tired, you eat more. It’s your body’s way of trying to keep up your energy. Being sleep-deprived also messes with the hormones in your brain that control your appetite, making you hungrier. When you’re tired, you may eat unhealthy foods that can pack on the pounds.
6 – Get more done
Sleep boosts your energy and brain levels. If you’re sleeping well, you’ll be more productive at work, home, and school. You’ll be able to concentrate better, retain new information, and better recall your stored memories. Sleep improves your mood so that you feel better and are ready to tackle new projects.
7 – Athletic benefits
An athlete’s body works harder than other people’s bodies. They need more calories and extra sleep. A study done by the National Sleep Foundation suggests that athletes need 10 hours of shut-eye every night. Getting an adequate amount of sleep improves athletic performance, including:
- More energy
- Faster speeds
- Better performance
- Better coordination
- Increased mental function
8 – Lower inflammation
Getting enough rest links to a reduction in inflammation in the body. Poor sleep is associated with inflammation dysfunction, especially in women, including rheumatoid arthritis, digestive system, and renal disease.
9 – Sleep increases longevity
Sleep has therapeutic and healing abilities. It builds and regenerates your cells, helps give your body rest, and removes toxins. A good night’s slumber can restore your hormonal and metabolic systems. All these things add up to a healthier, longer life.
10 – Slows down aging
Besides living longer, a healthy night’s sleep can affect your body’s aging process. Your skin produces collagen, the elastic protein in your skin, while you rest. Collagen prevents sagging and wrinkling of your skin. So, the more you rest you get, the more able your skin is to produce collagen.
Final Thoughts on Getting Sleep to Avoid Depression
Sleep is essential to your health. You need it for good brain function, a healthy heart, and to lower your inflammation. It helps you maintain your weight and stay productive. If you want to retain your youth and live longer, try to get at least seven to nine hours of sleep every night. Sleep is a natural remedy to feel better and look better.