When women reach a certain age, they experience menopause. While it is common knowledge, not many people know what happens to your body when you experience it. It causes many changes, resulting in a variety of symptoms.
Menopause can increase the risk of osteoporosis and other conditions. While it’s a normal part of life, it’s a milestone that signifies the time to watch out for other health issues. Do whatever you can to prevent worsening symptoms.
Learning all you can about this time in life can help you handle it gracefully. You’ll know what to expect and find comfort in understanding what’s happening to your body. Adjusting to the hormonal changes will be challenging, but you can do it.
What is Menopause?
Menopause signifies the end of a woman’s fertility cycle. It is safe to say you’re menopausal when your periods have stopped for a consecutive year. Their ovaries no longer produce estrogen and progesterone, both essential to fertility.
Most women stop having periods between 45 and 55, but that’s not always the case. Sometimes the beginning stages can begin years before periods stop, too. In other cases, women will continue having their periods into their late 50s.
The Difference Between Perimenopause and Menopause
Perimenopause is the time right before menopause begins when the transition starts. Hormone production starts to decline, causing some of the symptoms and causing an irregular menstrual cycle. The period doesn’t stop entirely during this stage, and women can still get pregnant.
When your periods cease completely, you’ll have officially entered the menopausal stage. It’s hard to know when it’s happening because periods might be irregular before they stop. You must wait a year to know for sure, but you’ll experience the common symptoms of the change.
It is also essential to discuss postmenopause, the third and final stage. Once you’ve gone twelve months without a period, you’re referred to as postmenopausal. After a year without periods, any vaginal bleed is abnormal.
What Causes Premature Occurrences
While menopause occurs naturally with age, it can also stem from other causes. These instances include surgery such as a hysterectomy, disease treatment, or an illness. When the reason isn’t natural, it is induced menopause.
A condition called premature ovarian failure can also cause early failure. It occurs when ovaries stop releasing eggs prematurely, and the hormone levels change. When premature ovarian failure causes perimenopause, it’s another example of induced menopause.
Additionally, some sources indicate that the age of onset is genetically predetermined. However, things like chemotherapy or smoking can speed up ovary decline, causing it to occur early.
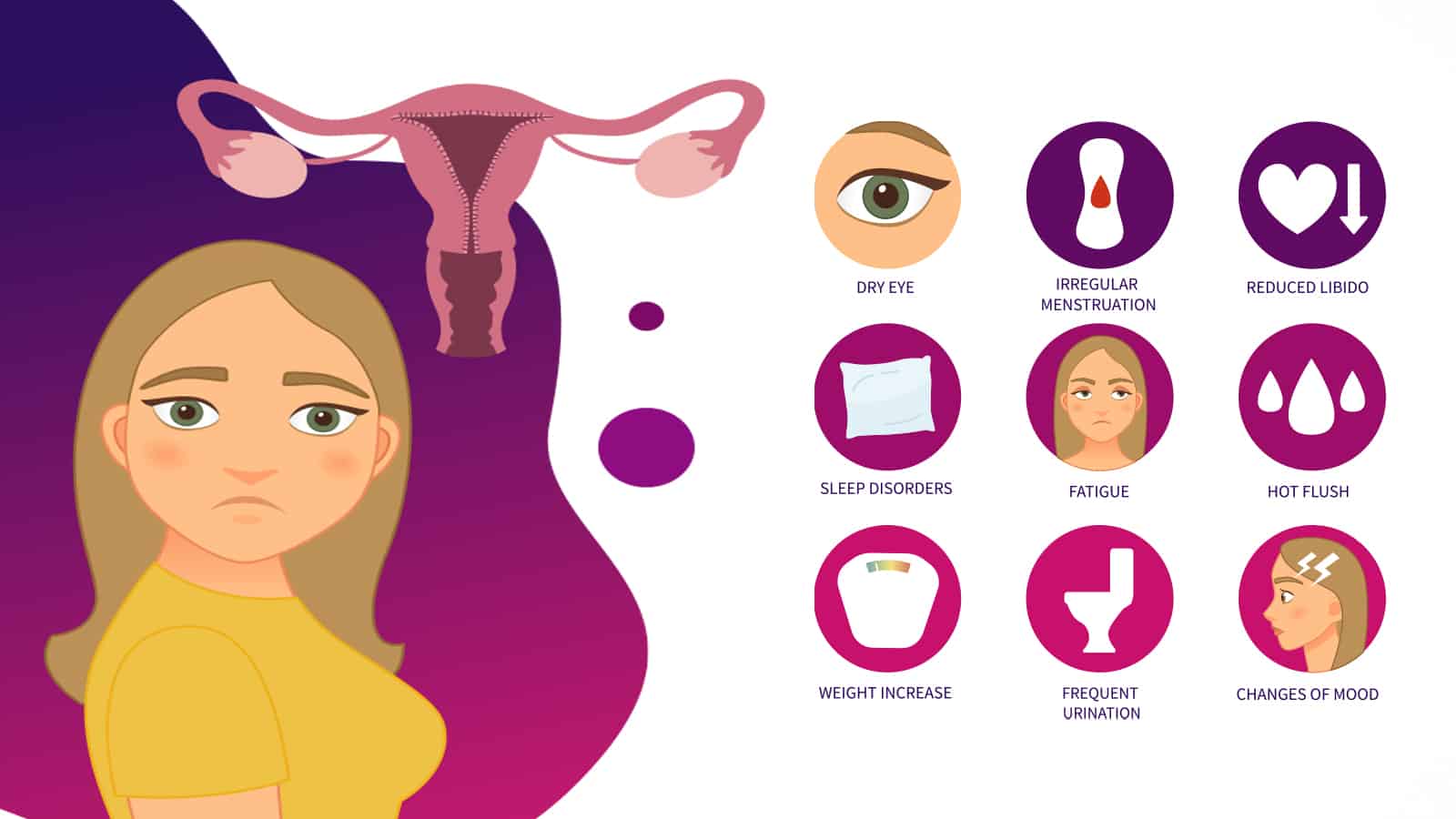
Signs and Symptoms of Menopause
Decreased production of estrogen and progesterone in the ovaries leads to many symptoms. These symptoms include:
- Irregular or nonexistent menstrual cycle
- Hot flashes
- Weight gain
- Vaginal atrophy and dryness
- Mood swings and unexplained irritability
- Decreased sex drive
- Sweating
- Racing heart
- Frequent headaches
- Trouble sleeping
- Discomfort during sex
- Sore breasts
- Frequent need to urinate
- Dry eyes, skin, or mouth
The later stages include all of the above symptoms, but also a few others, including:
- Fatigue
- Depression
- Muscle and joint pains
- Crankiness
- Hair loss
Everyone’s symptoms are different, so some might require medical attention and others don’t. You can discuss your situation with your doctor to determine the best course of action. What works for other people might not work for you, even if you are in the same family.
What Happens to Your Body in Menopause
When women are born, they already have their eggs stored in their ovaries, and they won’t produce more. Over the years, the ovaries produce estrogen and progesterone, releasing eggs once a month. The release of these eggs is called ovulation, when menstruation occurs.
When the body stops producing estrogen and progesterone, ovaries stop releasing eggs, and menstruation stops. It leads to many other changes in the body, drastically changing a woman’s life.
Your Body Temperature Rises
When you experience a hot flash, your body temperature rises quickly, making you uncomfortable. It affects the top half of your body, and your skin might become red or blotchy. Increased body temperature causes sweating, heart palpitations, and dizziness.
Hot flashes can occur multiple times a day, but you can learn your triggers and avoid them. Common triggers include:
- Drinking alcohol
- Consuming caffeine
- Eating spicy foods
- Being in a hot environment
- Experiencing stress
It Affects Bone Health
When estrogen production declines, it affects the calcium in your bones, too. As the calcium decreases, it interferes with bone density, causing osteoporosis. This condition makes you more likely to suffer from hip, spine, and other bone fractures, and bone loss accelerates.
You want to make sure to eat plenty of foods with calcium, including dairy products and leafy greens. Another way to keep your bones healthy is to take daily vitamin D supplements.
It Links to Heart Disease
Menopause can cause dizziness or cardiac palpitations, contributing to heart disease. The low estrogen levels affect the retention of flexible arteries, impacting blood flow.
You can reduce your chances of developing heart conditions by doing the following:
- Watch your weight
- Exercise regularly
- Eat a well-balanced, healthy diet
- Stop smoking
You Might Gain Weight
Hormonal changes can cause you to gain weight, and aging contributes, too. When menopausal, you might notice that you put on some pounds, but it doesn’t have to happen. Be extra vigilant about eating a healthy diet and exercising regularly.
Diagnosis of Menopause
You will likely suspect that you’re menopausal when your menstrual cycles stop and you experience other symptoms. Discuss the experience with your doctor, and they might make a diagnosis based on what you told them. It will help track your periods and share the patterns with your doctor.
If you’ve had a hysterectomy or an endometrial ablation, you won’t be able to use your periods as a way to tell. Your period ceases after these procedures, so you’ll have to watch for the other symptoms instead. The most telling sign you’ll notice is hot flashes.
Additionally, a doctor can request blood tests to check your hormone levels. A decline in your thyroids can cause irregular periods and cause similar symptoms. Your doctor might check to rule out a thyroid issue instead.
A doctor might also test for follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) because it increases when you’re getting close. They might also do an estradiol test showing how much estrogen your ovaries produce, allowing a doctor to recognize a failure. Checking estrogen levels can also show if you’re at risk of osteoporosis, and a bone density test might follow.
Finally, the anti-Mullerian hormone (AMH) test gives insight into the eggs in your ovaries. Your body produces it in your reproductive tissues. When it declines, it indicates an ovary failure.
How to Ease Menopause Symptoms
While the symptoms are unpleasant, there are ways you can treat them. They will go away eventually, but you don’t have to suffer through them right now. It’s sometimes as simple as making lifestyle changes, and the sooner you start, the better you’ll be.
One of the ways to ease the symptoms is to make healthy lifestyle changes. Eliminate unhealthy habits like smoking and excess drinking, and avoid caffeine or spicy foods. If you’ve noticed any other triggers, do what you can to avoid those, too.
Additionally, dress in layers to help with hot flashes no matter where you are. If you notice mental health issues such as depression, you’ll want to address them immediately. Some people use meditation and relaxation techniques to reduce stress and improve their symptoms.
Other healthy lifestyle changes you can try include the following:
- Weight loss or management
- Regular exercise
- Reduce the room temperature
- Drinking a cold glass of water to ease hot flashes
- Use a lubricant for vaginal dryness
- Do Kegel exercises
- Acupuncture
- Breathing exercises
Doctors can prescribe medication, but it isn’t necessary for everyone. It depends on the severity of your symptoms, bone loss, and overall health. However, it’s always best to make lifestyle changes to see if it helps first.
Your doctor might also use combination hormone therapy (HT) or replacement therapy (HRT). Both treatments help stabilize levels and help with night sweats and hot flashes, and they can help prevent osteoporosis. Some people shouldn’t use replacement therapy, so it’s essential to be open and honest with your doctor.
Final Thoughts on Science Explains What Happens to Your Body When You Go Through Menopause
As a natural part of a woman’s life, understanding menopause is essential. As hormones fluctuate, you’ll experience many changes that might be hard to handle at first. Easing the symptoms can make all the difference, and you can also do things to stay healthy throughout.
Lifestyle changes are often all it takes to overcome all the changes occurring in your body. However, discuss your symptoms with your doctor so that they can tell you if what you’re experiencing is normal.
Knowledge is power, and understanding what’s going on with your body will make you feel better. You don’t have to be afraid of this time if you apply what you know to make the milestone more comfortable.