Serotonin syndrome occurs when specific medications overly inhibit your body’s natural serotonin production.
For those who are not familiar with serotonin, it is a chemical that our bodies produce to allow brain cells and various nervous system cells to function optimally and communicate with each other.
Commonly found in the digestive system, serotonin also plays a critical role in regulating mood as well. This chemical is essential to our health and overall wellbeing. However, too much can lead to serotonin syndrome. This condition triggers intense nerve cell activity. Then, it gives way to a wide range of symptoms, some of which can be more severe than others.
In this article, we’ll explore the etiology of serotonin syndrome and treatments that are available to those struggling with the condition.
WHAT CAUSES SEROTONIN SYNDROME?
Typically, serotonin syndrome often occurs when an individual takes antidepressants or similar psychotropic medications for the first time. Or, it happens when a patient suddenly increases the amount that they are taking. Also, note that this condition is not limited to psychotropic medications only. In fact, any number of drugs or supplements may trigger this response.
That aside, symptoms synonymous with mildly serotonin levels will often resolve themselves within 1 to 2 days after an individual has stopped taking their medication or has lowered the dosage that they are taking. However, in some cases, medical attention may be necessary.
WHAT MEDICATIONS CAN CAUSE ELEVATED SEROTONIN LEVELS?
When it comes to high serotonin levels, several medications can contribute to the condition. Some of the most common include
MONOAMINE OXIDASE INHIBITORS
Commonly referred to as MAOIs, monoamine oxidase inhibitors are a class of drugs that were first introduced in the 1950s and are often prescribed to treat depression and anxiety.
Some of the most popular MAOIs include Nardil, Parnate, Marplan. These medications boost serotonin levels, which, in turn, elevate mood and improve brain cell communication.
SELECTIVE SEROTONIN REUPTAKE INHIBITORS
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are a specific class of medication that truly live up to their name in that they boost low serotonin levels. Similar to MAOIs, SSRIs treat depression as well as anxiety; some of the most popular SSRIs include Effexor, Cymbalta, Prozac, and Paxil. It is worth noting that the only SSRI anti-anxiety medication known to spike serotonin levels is buspirone.
PAIN RELIEVERS
While this is not the case with all pain relievers, certain prescription-based pain medications can cause a spike in serotonin levels, some of which include fentanyl, tramadol, meperidine, and pentazocine.
ANTIEMETICS
Surprisingly, certain prescription-based medications commonly prescribed to treat nausea can also lead to the onset of serotonin syndrome-related symptoms, some of the most common being Zofran, Reglan, and Kytril. It is also worth noting that some over-the-counter nausea medications can trigger the condition as well.
MIGRAINE MEDICATION
Similar to prescription-based pain relievers, certain prescription migraine medications can also cause serotonin syndrome-related symptoms. Some of these medications include Axert, Amerge, Maxalt, and Zomig.
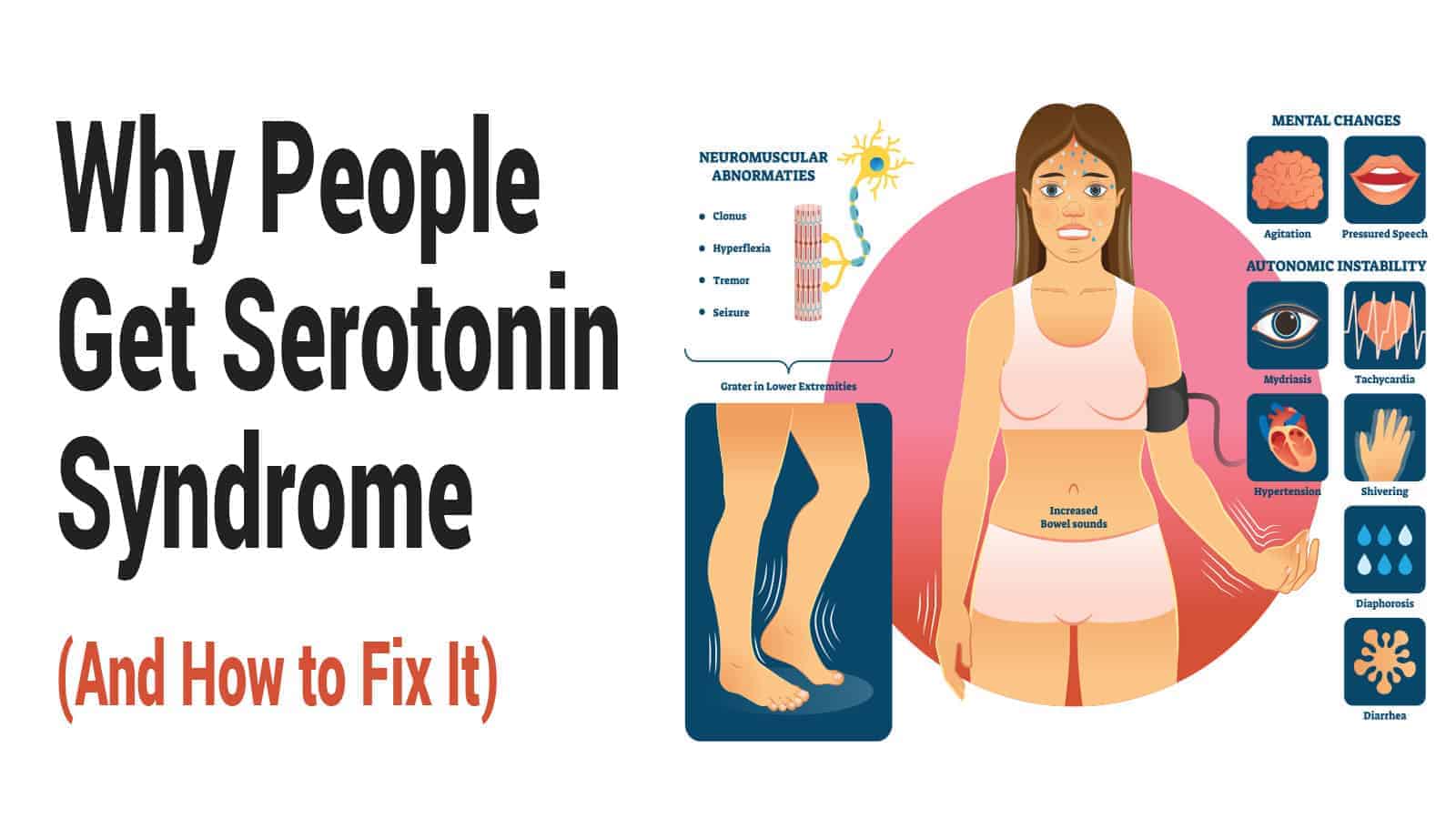
WHAT ARE THE SYMPTOMS OF HIGH SEROTONIN LEVELS?
When an individual takes a new medication or suddenly ups the dose on a drug they are already taking, they generally experience serotonin syndrome-related symptoms within a few hours. Some of the most common symptoms include
- Irritability
- Confusion
- Restlessness
- Headaches
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Profuse sweating
- Dehydration
- Changes in body temperature
- Heart palpitations
- A decline in muscle coordination
In extreme cases, it is not unheard of for individuals with elevated serotonin levels to also experience high fevers, seizures, and loss of consciousness. As such, the FDA (Food and Drug Administration) has urged drug manufacturers to include warning labels on all medications that are likely to trigger the condition.
TOP 7 RISK FACTORS FOR HIGH SEROTONIN LEVELS
Although taking new medications or suddenly upping the dose of certain medications can contribute to high serotonin levels, there are other risk factors worth noting:
1. ILLEGAL DRUGS
Along with the many health problems that are caused by illicit drug use, serotonin syndrome is yet another one that many individuals will encounter. Some of the illicit drugs known to trigger serotonin syndrome symptoms include methylenedioxy-methamphetamine (ecstasy), lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD), and cocaine. It is also worth noting that marijuana use can boost serotonin levels as well.
2. SUPPLEMENTS
In most cases, supplements can be a great way to provide your body with the nutrients that you don’t receive from whole foods, which can help improve or maintain your overall health. However, it’s entirely possible to experience too much of a good thing. According to some studies, excessive amounts of dietary supplements, namely St. John’s wort, nutmeg, ginseng, and L-glutamine, can cause serotonin syndrome, especially when taken with antidepressants.
3. COMBINING MEDICATIONS
Similar to combining dietary supplements with antidepressants, the combination of pain medications and antidepressants can also result in serotonin syndrome-related symptoms. Several studies show that those who take antidepressants along with migraine medication or opioids, for example, are more likely to develop the condition.
4. OVERDOSING ON MEDICATIONS
Whether the intent is to derive an intense high or something more malicious, taking excessive amounts of any serotonin-boosting medication can lead to serotonin syndrome and also endanger your life.
5. OVER-THE-COUNTER COLD AND COUGH MEDICATIONS
Although most of us would never think that over-the-counter medications could ever compromise our health, some of them can. According to some studies, over-the-counter cough and cold medicines that contain dextromethorphan, such as Mucinex DM and Delsym, for example, can cause serotonin syndrome if taken in large amounts.
6. TAKING NEW MEDICATIONS
Taking a new serotonin-boosting medication for the first time is the leading cause of elevated serotonin levels. If you notice serotonin syndrome-related symptoms after taking a new drug, you should schedule an appointment with your physician immediately.
7. UPPING THE DOSE ON MEDICATIONS
To avoid developing serotonin syndrome-related symptoms, it is always best to take prescription-based medications as directed by a physician. Similarly, you should carefully follow the recommended dosing indicated on any over-the-counter medications as well.
HOW DO DOCTORS DIAGNOSE HIGH SEROTONIN LEVELS?
When it comes to diagnosing serotonin-related syndrome symptoms, there is no specific medical test that can confirm whether or not an individual has developed the condition. Instead, physicians will inquire about their patient’s symptoms, medical history, and whether or not they are taking any supplements or engaging in illegal drug use. Additionally, doctors might order a physical exam to rule out other health conditions.
WHAT TREATMENTS ARE AVAILABLE TO THOSE WITH ELEVATED SEROTONIN LEVELS?
If an individual experiences mild serotonin syndrome-related symptoms, they will usually dissipate once their serotonin levels return to a normal and healthy range. As such, medical attention is generally not needed. However, in severe cases, they may need to be hospitalized. Along with advising patients to stop taking the medication responsible for the condition, most physicians will start patients on the following treatments:
Benzodiazepines – To help patients cope with agitation or seizures caused by a spike in serotonin levels, many physicians will prescribe Ativan, Valium, Xanax, or other benzodiazepine medications to their patients.
Intravenous fluids – Because dehydration is a common symptom of elevated serotonin levels, many physicians will provide intravenous fluids, namely electrolytes, to help keep their patients hydrated.
Cyproheptadine – In some cases, doctors will start patients on cyproheptadine hydrochloride. This medicine is a prescription antihistamine that blocks serotonin production.
 ARE HIGH SEROTONIN LEVELS LIFE-THREATENING?
ARE HIGH SEROTONIN LEVELS LIFE-THREATENING?
In addition to being unpleasant, the symptoms associated with elevated serotonin levels can also be life-threatening. If an individual with high serotonin levels does not seek prompt medical attention, the condition can lead to a loss of consciousness and can be fatal. On that note, if an individual purposely overdoses on antidepressants or other serotonin-boosting medication, the results will likely be lethal. That said, there are seldom any remaining long-term effects after serotonin levels have returned to normal.
 FINAL THOUGHTS ABOUT AVOIDING SEROTONIN SYNDROME
FINAL THOUGHTS ABOUT AVOIDING SEROTONIN SYNDROME
In summary, elevated serotonin levels can trigger a wave of unpleasant symptoms. And, when not treated, these can be fatal. The best way to reduce your chances of developing this severe condition is by speaking with your doctor about possible risk factors and taking your medication as prescribed.
You must also talk with your physician if you need to take multiple medications to treat two or more health problems. After all, combining medicines triggers an increase in serotonin production.