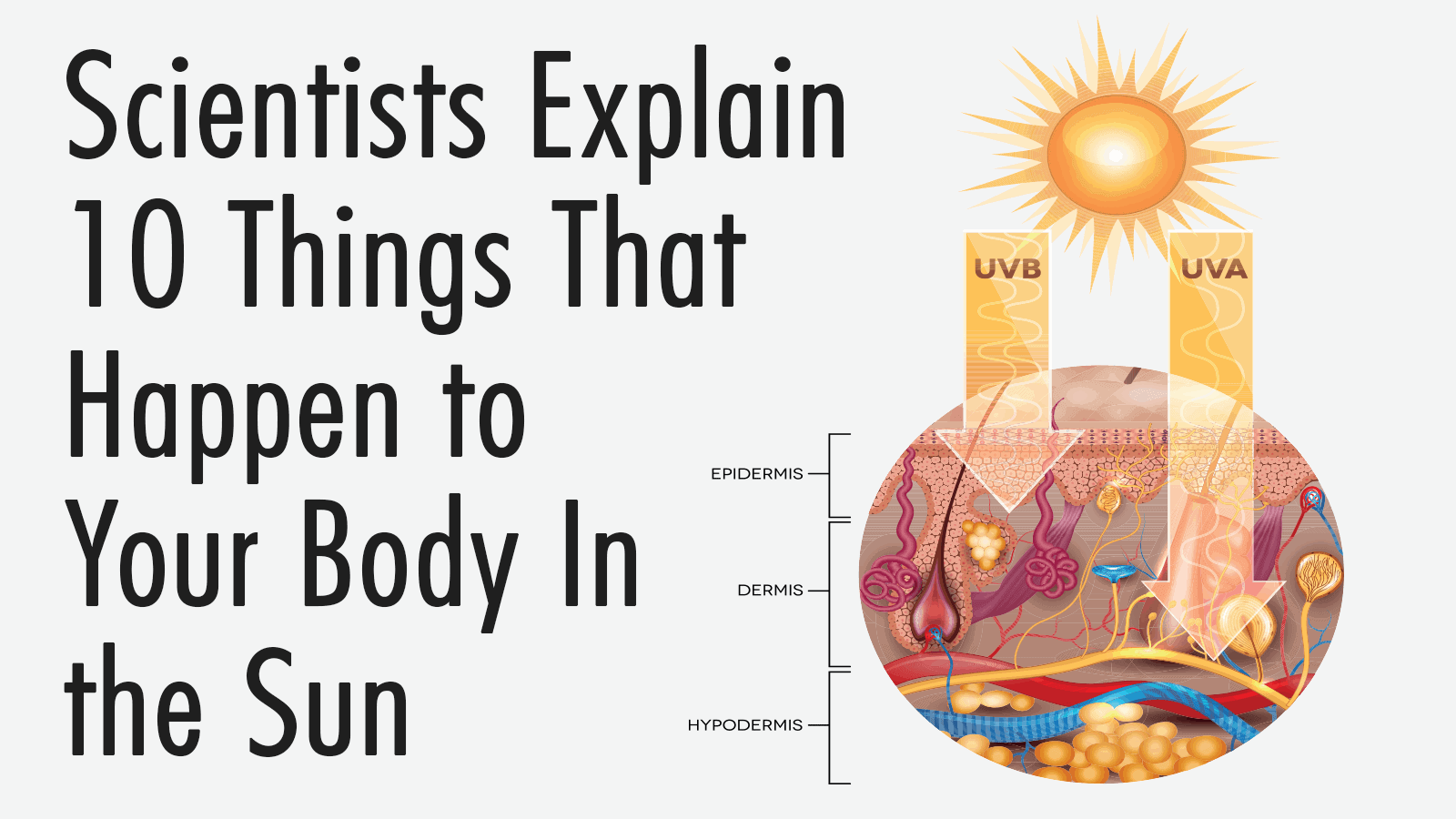
“Turn your face to the sun and the shadows fall behind you.” – Unknown
People have been discouraged from staying under the sun for too long because of its negative effects on the skin. However, as sunshine is the most powerful natural source of vitamin D, there are in fact many health benefits to basking under the sun. Here are some scientific facts that explain what may happen to your body in the sun.
Here Are 10 Things That Happen to Your Body in the Sun
1. The sun literally brightens people’s moods.
Despite its harmful UV rays, the sun can also trigger feel-good hormones that make people feel better. This perhaps explains why despite several warnings that sunbathing can cause cancer, people still look forward to going to the beach in the summer to get a tan. According to Harvard Medical School experts, the sun facilitates the release of endorphins that raise your body’s serotonin levels, which is also known as the happy hormone. It’s similar to the effects of exercising, meditation, thinking positive thoughts, and eating serotonin-boosting foods.
2. Sunshine impacts people with Seasonal Affective Disorder.
There’s such a thing as a Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD) and it’s a type of depression that develops during the colder months. Psychiatry experts confirm that some people get the blues during winter because their genetics are so sensitive to the lack of sunshine. However, a little bit of warmth could help combat depression as effectively as medication. For severe cases, experts recommend light therapy for at least 30 minutes to help manage this mood disorder and relieve depression.
3. Vitamin D from the sun nourishes the bones.
Nearly 40 percent of Americans lack vitamin D and there are health consequences to this deficiency. Low vitamin D levels can lead to the development of osteoporosis, muscle weakness, and cancer. For bone health, experts recommend 13 to 15 minutes of sunlight exposure during the middle of the day, when the UVB rays are most intense. The body needs 600 IU of vitamin D every day. At noontime, the sun delivers at least 10,000–20,000 IU of vitamin D.
4. The sun can boost the heart’s health.
An analysis of four million people in 2013 (“the entire Danish population”!) led a scientist from Denmark to conclude that sunlight can protect and boost the heart’s health. Ironically, the study learned that people who suffered from skin cancer actually lowered their heart attack risks. The experts said that vitamin D might have something to do with this as well, but the research needed further probing to confirm the hypothesis.
5. The sun can be a remedy for acne.
While the sun has a bad rep for causing skin dryness, wrinkles, and skin cancer, it might actually be good for treating acne. Sunshine works to suppress the bacteria that cause acne development and redness. However, you still need to control sun exposure and protect your skin with sunscreen and Aloe Vera. In this case, experts say that the disadvantages of sun exposure might still outweigh the benefits.
6. Sunlight can extend your life expectancy.
After following some 30,000 Swedish women for 20 years, scientists at Karolinska University Hospital and Lund University learned that those who avoided sun exposure because of restrictive health guidelines shortened their lifespan by six months to two years. The women who had the most sunlight, meanwhile, lowered their heart disease risk. Experts, however, are still unclear on what sunlight has to do with life expectancy but it’s possibly linked the benefits of vitamin D.
7. Sunshine can alleviate your stomach problems.
People who reside in sunny states experienced 52 percent fewer stomach problems like inflammatory bowel disease, ulcerative colitis, or Crohn’s disease compared to those who live in the colder northern states in America. A European research discovered the discrepancy and cited that it’s likely because southerners get more vitamin D that can regulate inflammation and immunity to diseases.
8. Sunlight could lower breast cancer risks.
Women who regularly spent an hour under the sun for 10 years reportedly had fewer risks of breast cancer, as per a study in the Environmental Health Perspective journal. Experts, however, clarified that the risk reduction is small. Larger studies are needed to determine any proof that the effects are on the genetic level.
9. The sun can slow down multiple sclerosis progression.
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a debilitating condition that affects the central nervous system. In its more advanced stage, MS can damage the nerves, thus crippling a person’s movements, visions, speech, and body function. But a Harvard study found out that sun exposure improved the quality of life of patients with MS in areas that had higher UVB rays. However, a separate study in the journal Nutrients showed that the benefits of lowered MS risks were more evident in Caucasian patients only.
10. The sun may lower blood pressure.
Exposure to sunlight can increase the body’s nitric oxide, which can help open up the blood vessels. Volunteers of a study published in the Journal of Investigative Dermatology presented improved blood pressure levels with regular sun exposure during wintertime. Apparently, winter triggers an increase in hypertension cases, but the risks can be mitigated with sunlight.
Final thoughts
Despite the benefit, it bears noting that sunlight is still a very real threat to skin cancer. However, these studies from experts indicate that completely avoiding the sun is also not good for the body’s health. To reap the full benefits of sunlight, you must learn to strike a balance. Get natural vitamin D as regularly as possible but avoid sunburn by wearing protective clothing and sunscreen.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YeKgaiwOtXo